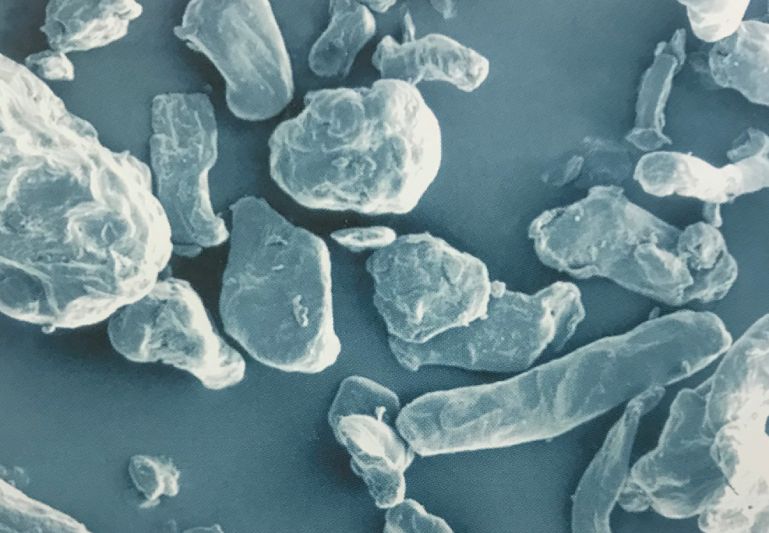
1. Chemical structure
Croscarmellose sodium (CCS) is a cross-linked polymer of carboxymethyl cellulose sodium.
2. Pharmacopoeia nomenclature
Croscarmellose sodium (BP; JP; PhEur; USP-NF).
3. Trade name – Manufacturer (Distributor of Vietnam)
Ac-Di-Sol; Nymcel ZSX; Pharmacel XL; Primellose, Solutab; Vivasol.
Some suppliers in Vietnam: Saphachem; FD&C; Dang Hung, Develing; IMCD.
4. General properties
Croscarmellose sodium (CCS) is a white or off-white powder that is odorless, insoluble in water, and nearly insoluble in ethanol. CCS can expand 4-8 times its original volume after 10 seconds in water due to its hydrophilic characteristics.
Wicking and swelling are both involved in the mechanism of action. The disintegration effect of CCS is greater when used with water-insoluble filler excipients due to its high permeability.
5. Incompatibility
CCS is incompatible with basic active ingredients/excipients, resulting in decreased tablet solubility after stability testing. CCS is incompatible with strong acids, soluble iron salts, and certain metals such as aluminum, mercury, and zinc.
6. Main application
CCS is a super-disintegrant commonly used in solid dosage forms such as tablets, capsules, and granules.
- In tablet formulation, CCS can be used for both wet granulation and direct compression methods. CCS should be added in equal amounts during both the granulation and final mixing phases of the wet granulation method. CCS is commonly used at 2% (w/w) for direct compression and 3% (w/w) for wet granulation.
The amount of Croscarmellose sodium used in the tablet formula ranges from 0.5 – 5%. - In capsules: from 10% to 25%.
- In dispersible tablets: at least 3%
- In powders and granules: from 1 to 2%
A number of top brand-name drugs contain this excipient:
Viagra (Sildenafil citrate); Advil (Ibuprofen); Panadol (Paracetamol); Lipitor (Atorvastatin); Celebrex (Celecoxib).
7. Personal experience
- The super disintegrant effect of CCS can be decreased when combined with highly hygroscopic excipients, such as Sorbitol, in wet granulation and direct compression methods.
- In the 0.1N HCl, the level and rate of water absorption by CCS decreases due to its ionization properties.
- Tablet disintegration is decreased because CCS is incompatible with several alkaline excipients. The ester cross-link of CCS can be partially to totally hydrolyzed in an alkaline environment (formula having strong alkaline excipients, pH>9) to generate polymers that are extremely soluble in water, resulting in the formation of a highly viscous layer when the tablet absorbs water.
- When CCS and Sodium starch glycolate are combined, the disintegration time of the tablet may increase, especially for slow-disintegrating tablets.
- When conducting incompatibility investigations using HPLC methods, CCS may reduce the rate of API recovery. This can be explained by the ionic nature of CCS and the partial ionization of API during the mobile phase. The ionized API forms a less soluble API-CCS salt through ionic bonds with CCS.
REFERENCES:
- Incompatibility of croscarmellose sodium with alkaline excipients in a tablet formulation
- Investigation of Excipient Compatibility and Associated Degradations for the Formulation Development of a Small Molecule Pharmaceutical Compound
- R. C. Rowe, P. J. Sheskey, and S. C. Owen, “Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients Fifth Edition.”